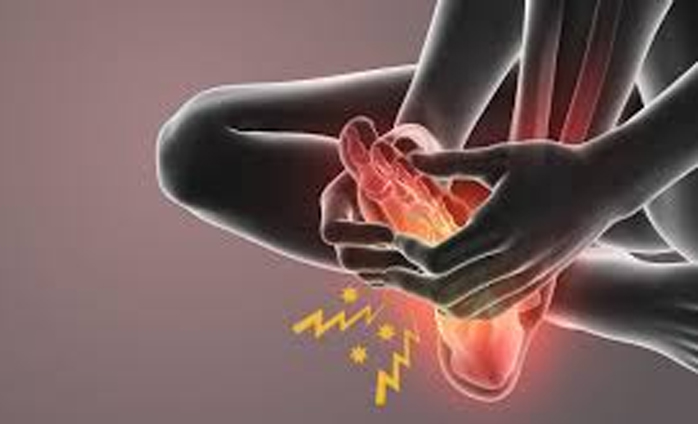
Neuropathy, also known as peripheral neuropathy, is a condition resulting from damage to the peripheral nerves, which transmit signals between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body. This damage can cause a variety of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, burning sensations, and muscle weakness, typically starting in the hands and feet and potentially spreading to other areas. Neuropathy can significantly impact a person's quality of life, leading to difficulties with balance, coordination, and performing daily activities.
Several factors can cause neuropathy, including diabetes (diabetic neuropathy), infections, injuries, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders, and exposure to toxins. Treatment for neuropathy focuses on managing the underlying cause, alleviating symptoms, and improving function. Medications such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants can help manage pain and discomfort. Additionally, physical therapy may be prescribed to enhance strength, balance, and coordination. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco, can also help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing neuropathy effectively, reducing symptoms, and preventing further nerve damage. Through a combination of medical treatment, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, individuals with neuropathy can achieve better symptom control and an improved quality of life.

